Analytical Chemistry
Exercise 1
Solution 1.
(a) Ferrous salts : Light green
(b) Ammonium salts : Colourless
(c) Cupric salts : Blue
(d) Calcium salts : Colourless
(e) Aluminium salts : Colourless
Solution 2.
(a) Cu(OH)2
(b) ZnO
(c) NaOH
(d) NH4OH
(e) Na+, Ca2+
(f) Fe2+, Mn2+
(g) Aluminium
(h) Zn(OH)2 and Al(OH)3
(i) PbO
(j) Ammonium ion
Solution 3.
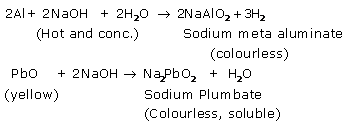
Solution 4.

Solution 5.

Solution 6.
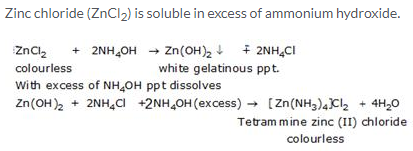
Solution 7.
(a) ZnCl2
(b) Zn(OH)2
Solution 8.
(a) PbO
(b) ZnO
(c) K2ZnO2
Solution 9.
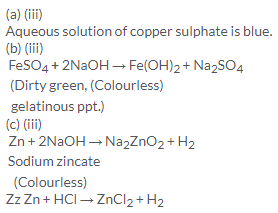
Solution 10.
When freshly precipitated aluminum hydroxide reacts with caustic soda solution, whitesalt of sodium meta aluminate is obtained.![]()
Solution 11.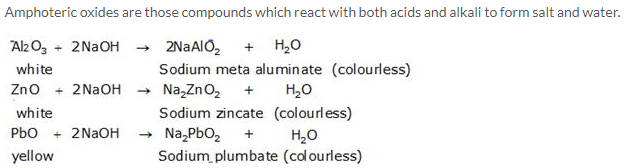
Solution 12.
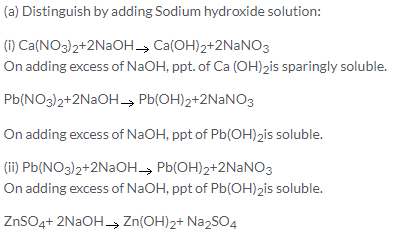
With excess of NaOH, white gelatinous ppt. of Zn (OH)2 is soluble. So, these two cannot be distinguished by NaOH alone. However white ppt. of Pb(OH)2 is readily soluble in acetic acid also.
(i) On addition of NH4OH to calcium salts no precipitation of Ca(OH)2 occurs even with addition of excess of NH4OH because the concentration of OH–ions from ionization of NH4OH is so low that it cannot precipitate the hydroxide of calcium.
Pb(NO3)2+2 NH4OHPb(OH)2+2NH4NO3
Solution 13.
Lead carbonate is dissolved in dilute nitric acid and then ammonium hydroxide is added to it. A white precipitate is formed which is insoluble in excess.
Zinc carbonate is dissolved in dilute nitric acid and then ammonium hydroxide is added to it. A white precipitate is formed which is soluble in excess.
Solution 14.
Reagent bottles A and B can identified by using calcium salts such as Ca(NO3)2.
On adding NaOH to Ca (NO3)2, Ca (OH)2 is precipitated as white precipitate which is sparingly soluble in excess of NaOH.
Ca(NO3)2+2NaOH → Ca(OH)2+ 2NaNO3
Whereas, on addition of NH4OH to calcium salts, no precipitation of Ca(OH)2 occurs even with addition of excess of NH4OH because the concentration of OH–ions from the ionization of NH4OH is so low that it cannot precipitate the hydroxide of calcium.
So the reagent bottle which gives white precipitate is NaOH and the other is NH4OH.
Intext Exercise
Solution 1.
(i) Analysis: The determination of chemical components in a given sample is called analysis.
(ii) Qualitative analysis: The analysis which involves the identification of the unknown substances in a given sample is called qualitative analysis.
(iii) Reagent: A reagent is a substance that reacts with another substance.
(iv) Precipitation: It is the process of formation of an insoluble solid when solutions are mixed. The solid thus formed is called precipitate.
Solution 2.
(i) Yellow
(ii) Colourless
(iii) PaleGreen
(iv) Colourless
(v) Colourless
Solution 3.
(i) Fe3+
(ii) Cu2+
(iii) Cu+2
(iv) Mn2+
Solution 4.
(i) Ca(OH)2
(ii) Fe(OH)2 and Cu(OH)2
(iii) Zn(OH)2 and Pb(OH)2
Solution 5.

Solution 6.
NH4OH and NaOH can be distinguished by using calcium salts.
For example on adding NaOH to Ca(NO3)2, Ca(OH)2 is obtained as white precipitate which is sparingly soluble in excess of NaOH.
Ca(NO3)2 + 2NaOH → Ca(OH)2 + 2NaNO3
On addition of NH4OH to calcium salts, no precipitation of Ca(OH)2 occurs even with the addition of excess of NH4OH.This is because the concentration of OH– ions from the ionization of NH4OH is so low that it cannot precipitate the hydroxide of calcium.
Solution 7.
(i) Fe(OH)2 and Pb(OH)2
(ii) Cu(OH)2 and Zn(OH)2
Comments
Post a Comment